Week four of Our National Heart Month Series continues this week as we discuss heart attacks in the elderly. A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, happens when the flow of blood that brings oxygen to a part of your heart muscle suddenly becomes blocked. Your heart can’t get enough oxygen and if blood flow is not restored quickly, the heart muscle will begin to die. The elderly are at the greatest risk, as heart attacks more commonly occur in people over the age of 60 years.
Heart attacks are very common. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than 800,000 people in the United States have a heart attack each year.
What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
If you are having a heart attack, you may experience one or more of the symptoms below.
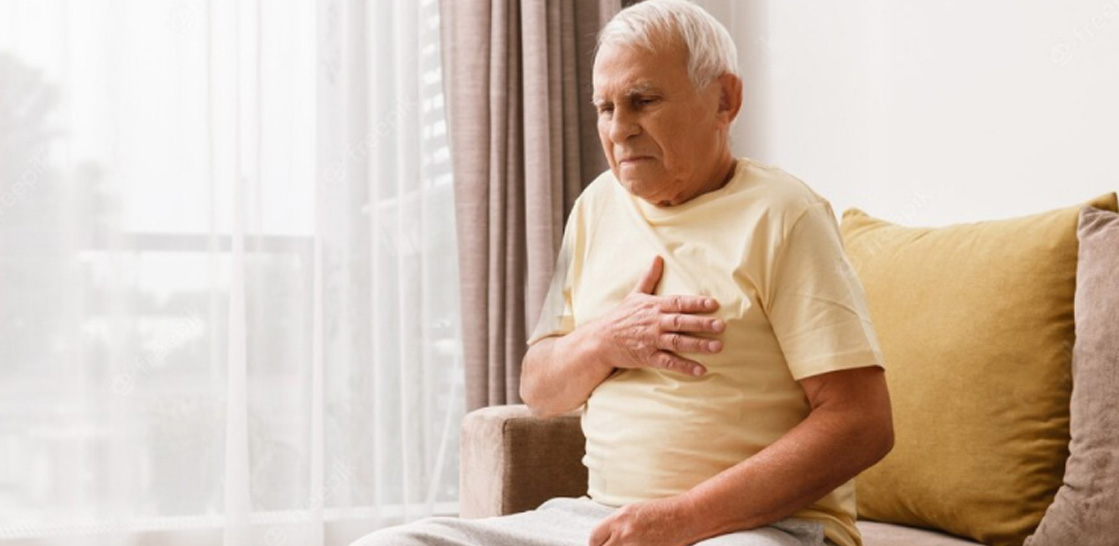
- Chest pain, heaviness, or discomfort in the center or left side of the chest (this is the most common symptom)
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms, your back, shoulders, neck, jaw, or above your belly button
- Shortness of breath when resting or doing a little bit of physical activity (this is more common in older adults)
- Sweating a lot for no reason
- Feeling unusually tired for no reason, sometimes for days (this is more common in women)
- Nausea (feeling sick to the stomach) and vomiting
- Light-headedness or sudden dizziness
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
It is also possible to have mild symptoms or even no symptoms at all and still have a heart attack.
If you think you are having a heart attack, do not hesitate to call or have someone else call 9-1-1.